COURSE:
NURS-6630N: Approaches to Treatment
This week, you will create a Medication Study Guide to share with your peers. This guide is intended to be a useful learning tool for you to use as you prepare for your clinical courses.
You will be assigned one of the following medications to create your guide:
| Chlorpromazine | Fluphenazine | Haloperidol | Loxapine | Perphenazine |
| Aripiprazole | Asenapine | Clozapine | Iloperidone | Olanzapine |
| Paliperidone | Quetiapine | Risperidone | Ziprasidone | Lurasidone |
| Brexpiprazole | Cariprazine | Lumateperone | Benztropine | Propranolol |
| Deutetrabenazine | Valbenazine |
The Assignment
Create a 3- to 4-page (excluding visual elements) Medication Study Guide for your assigned psychotropic medication agents that may be utilized by you and colleagues for study. Your medication guide should be in the form of an outline and should include a title page, citations, and references. You should incorporate visual elements, such as concept maps, charts, diagrams, images, color coding, mnemonics, and/or flashcards. Be creative!
Note: Your Medication Study Guide should not be in the format of an APA paper.
Also Note: Your guide should be informed by the FDA-Approved and Evidenced-Based, Clinical Practice Guidelines Research.
Areas of importance that you should address—but are not limited to—include:
- Title page
- Description of the psychopharmacological medication agent, including brand and generic names, as well as appropriate FDA indication uses
- Any supporting, valid, and reliable research for non-FDA uses
- Drug classification
- The medication mechanism of action
- The medication pharmacokinetics
- The medication pharmacodynamics
- Appropriate dosing, administration route, and any considerations for dosing alterations
- Considerations of use and dosing in specific specialty populations, such as children, adolescents, elderly, pregnant people, those exhibiting suicidal behaviors, etc.
- Definition of half-life, why half-life is important, and the half-life for your assigned medication
- Side effects/adverse reactions potential
- Discuss clinical concerns with EPS and Tardive Dyskinesia
Note: Be sure to include screening tools that would be utilized. - Contraindications for use including significant drug to drug interactions
- Overdose considerations
- Diagnostics and labs monitoring comorbidities considerations
- Legal, ethical, and social considerations
- Pertinent patient education considerations
- References page
Solution
Patient Medication Guide: Deutetrabenazine
| Description of Deutetrabenazine
|
Brand name : Austedo, Austedo XR
Generic name: Deutetrabenazine FDA indication: v It is used to treat chorea that is associated with Huntington’s disease. v Also approved for tardive dyskinesia in adult patients (U.S. Food and Drug Administration, n.d |
| Non-FDA uses | v Studies have also reported that it can be used to treat tics associated with Tourette syndrome (Coffey et al., 2021) |
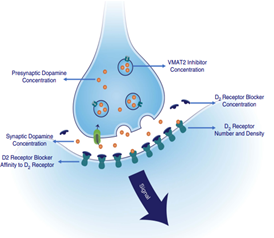
| Drug classification | This drug is a vesicular monoamine transporter2 (VMAT2) inhibitor. |
| Mechanism of action
|
Works by reducing the action of the action of VMAT2 thereby reducing the levels of monoamines in the synaptic cleft. Ideally, VMAT2 is involved in the packaging of monoamines such as norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine into vesicles. Deutetrabenazine metabolites namely the αdihydrotetrabenazine [HTBZ] and β-HTBZ) are considered as reversible inhibitors of VMAT2. Therefore, they lead to a decrease in the uptake of monoamines into the synaptic vessels as well as depletion of the monoamine stores (FDA, n.d.)
|
…………………………………….$10